Rising Concerns Over Anti-Islamism in India Amidst Political Shifts
Opposition Gains Power Amid Accusations of Anti-Muslim Bias
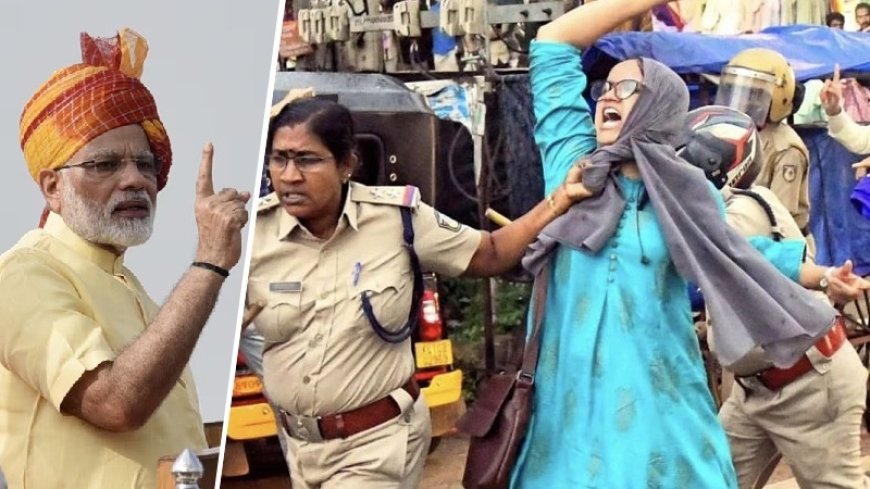

The recent Lok Sabha elections in India have significantly altered the political landscape, bringing opposition parties, including a notable number of Muslim representatives, into power. This shift comes as Prime Minister Narendra Modi embarks on his third term, with the voices of India's protesting minorities, particularly Muslims, growing increasingly prominent.
In the month following Modi's re-election, opposition parties have adopted a distinct tone in the Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha, emphasizing the need to address the grievances of India's Muslim minority. Calls have been made to re-examine policies and laws perceived as discriminatory against Muslims, aiming to restore rights and ensure equal treatment under the law.
Historical Context of Accusations
Since the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) first came to power in 2014, the Modi government has faced persistent accusations of marginalizing Muslims. Controversial changes to citizenship and marriage laws, perceived as targeting Muslims, have fueled these allegations. India's 200 million Muslims, the country's largest minority, have increasingly reported incidents of hate speech and discrimination.
Statements from Opposition Leaders
Prominent opposition figures, such as Asaduddin Owaisi, a member of the Hyderabad constituency, have been vocal in their criticism of the BJP. On July 3, Owaisi condemned the ongoing violence and oppression against Muslims, attributing Modi's political success to his association with Hindutva extremists. He described the situation as alarming, pointing to a series of violent incidents perpetrated by extremist Hindu groups.
Communist Party of India's Stance
The Communist Party of India (CPI) has also weighed in, condemning the recent spate of attacks on the Muslim community following the election results. The CPI highlighted actions such as the demolition and burning of mosques, restrictions on religious practices, and revocation of residency permits for Muslim immigrants as part of a broader pattern of oppression.
Specific Incidents and Broader Implications
Key incidents cited include the revocation of special autonomy for the Kashmir region, which has been a flashpoint for Muslim discontent, and the government's silence in the face of violent attacks by Hindu extremists. These measures have not only intensified domestic tensions but have also drawn international criticism, contributing to a perception of growing intolerance in India.
Global Reactions
The international community, particularly in predominantly Muslim countries, has expressed concern over the treatment of Muslims in India. This has led to a rise in latent animosity towards India, affecting its global image and diplomatic relations.
As India navigates this complex socio-political terrain, the challenge lies in addressing these deeply rooted issues and fostering an environment of inclusivity and respect for all its citizens.